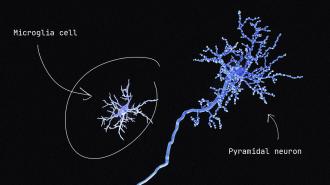
Seizures are like sudden electrical storms in the brain. Seizure disorders like epilepsy affect over 65 million people worldwide and can have profound effects on a person’s quality of life, cognitive function and overall well-being. Prolonged seizures called status epilepticus can cause lasting brain damage.
Specialized immune cells in the brain called microglia are activated during seizures to help clean up the damage. Researchers don’t fully understand exactly how these cells are involved in seizures. Some studies have found that microglia promote seizures, while other studies show the opposite.
I am a scientist who studies the roles that microglia play in seizures. My colleagues and I at the Eyo Lab at the University of Virginia wanted to investigate the possible protective function microglia serve during seizures and how they affect recovery.
We induced seizures in mice using three different methods – chemical, hyperthermic and electrical – and temporarily removed their microglia. In all three cases, we found that seizures worsened when these cells were absent. Mice without microglia also experienced significant weight loss and decrease in mobility compared with mice with microglia.
Our findings highlight the importance of microglia in safeguarding the brain during seizures and promoting recovery; but they also raise important questions about how these cells provide a protective rather than detrimental effect.
While removing all microglia allowed us to better understand their overall effects on seizures, it meant we were unable to fully assess their contributions in specific brain regions and how they interact with other cells. This is because removing microglia also affects the function of other brain cells. Future studies that more selectively modify microglia or alter their function in a controlled way could help researchers gain a more nuanced understanding of the role these cells play in seizures.
Researchers also don’t fully understand what specific molecules and signals microglia use to protect the brain during seizures. How well our findings apply to seizure disorders like epilepsy is also unclear. These knowledge gaps highlight the complexity of seizure disorders and the need for continued study.
Identifying strategies to harness the beneficial functions of microglia can help researchers develop better treatments that prevent long-term brain damage and enhance the quality of life of people with seizure disorders.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.