This is T-Minus, where we count down the biggest developments in space, from new rocket launches to discoveries that advance our understanding of the universe and our place in it. Humanity is reaching new heights in space exploration. Make sure you’re part of the journey by subscribing here.

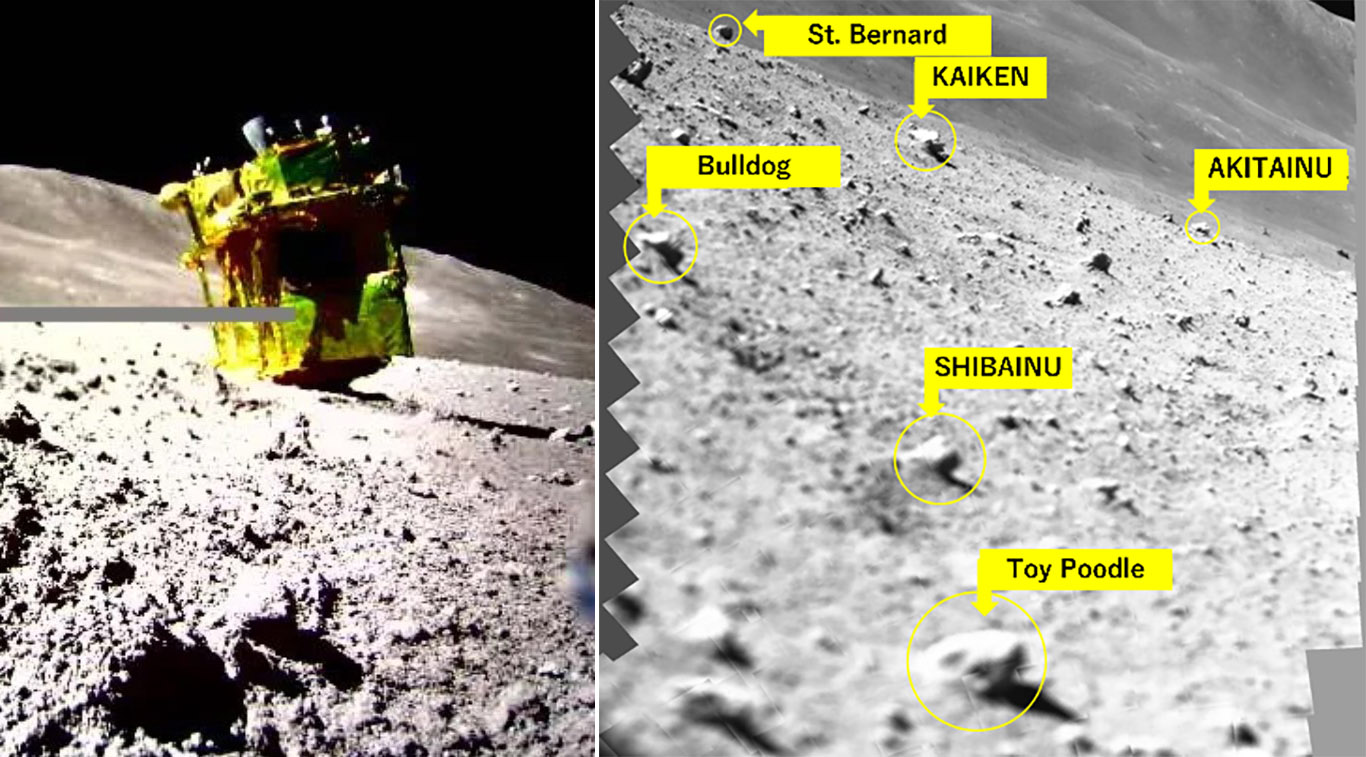
SLIM comes back to life
Japan joined the short list of nations that have landed on the moon when its Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) touched down on January 19 — but the success was bittersweet.
Due to an engine failure during its descent, SLIM landed on the moon upside down, and that positioning meant its solar panels were in a shadow and couldn’t charge. JAXA powered down the spacecraft with 12% left on its battery, but said it was hopeful the panels would start working in the future as the position of the sun in the lunar sky changed.
It seems the sun has cooperated as JAXA was able to reestablish communication with SLIM on January 28. It has since shared the spacecraft’s first image, which includes several rocks that JAXA has nicknamed after different dog breeds as an indication of their relative size.

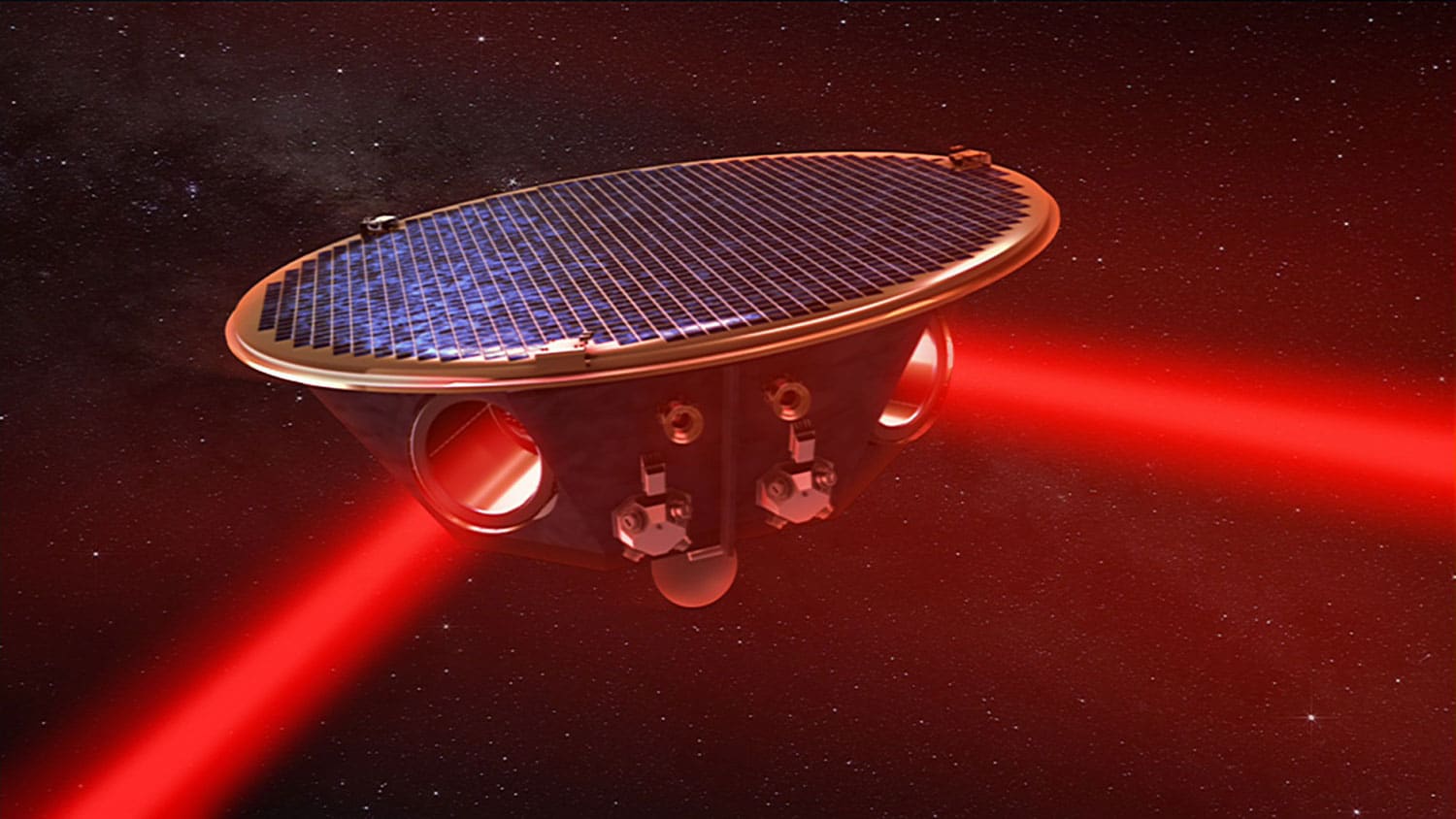
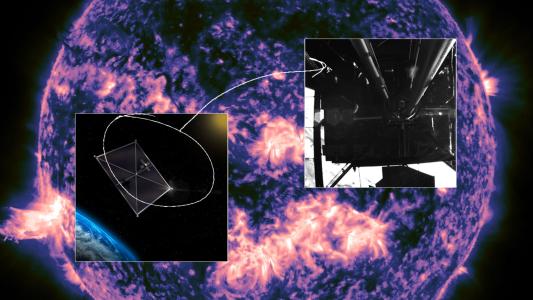
LISA gets the green light
The movement of massive objects in the universe can cause ripples in the fabric of space-time itself, called gravitational waves. Studying these waves can allow us to “see” events that aren’t visible through light-based observations, such as collisions between black holes.
Astronomers have been able to detect gravitational waves at ground-based observatories since 2015, but ESA has now greenlit the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) mission, which aims to place a gravitational wave detector in space for the first time.
LISA will consist of three spacecraft that follow Earth around the sun. While flying in a perfect triangle formation, they’ll shoot laser beams between themselves, and by measuring the distances the lasers travel, astronomers will be able to detect the presence of gravitational waves. Construction will begin in 2025, with the launch scheduled for 2035.
“LISA is designed to sense low-frequency gravitational waves that instruments on Earth cannot detect,” said Ira Thorpe, a scientist at NASA, which is serving as ESA’s collaborative partner on the mission. “These sources encompass tens of thousands of small binary systems in our own galaxy, as well as massive black holes merging as galaxies collided in the early universe.”
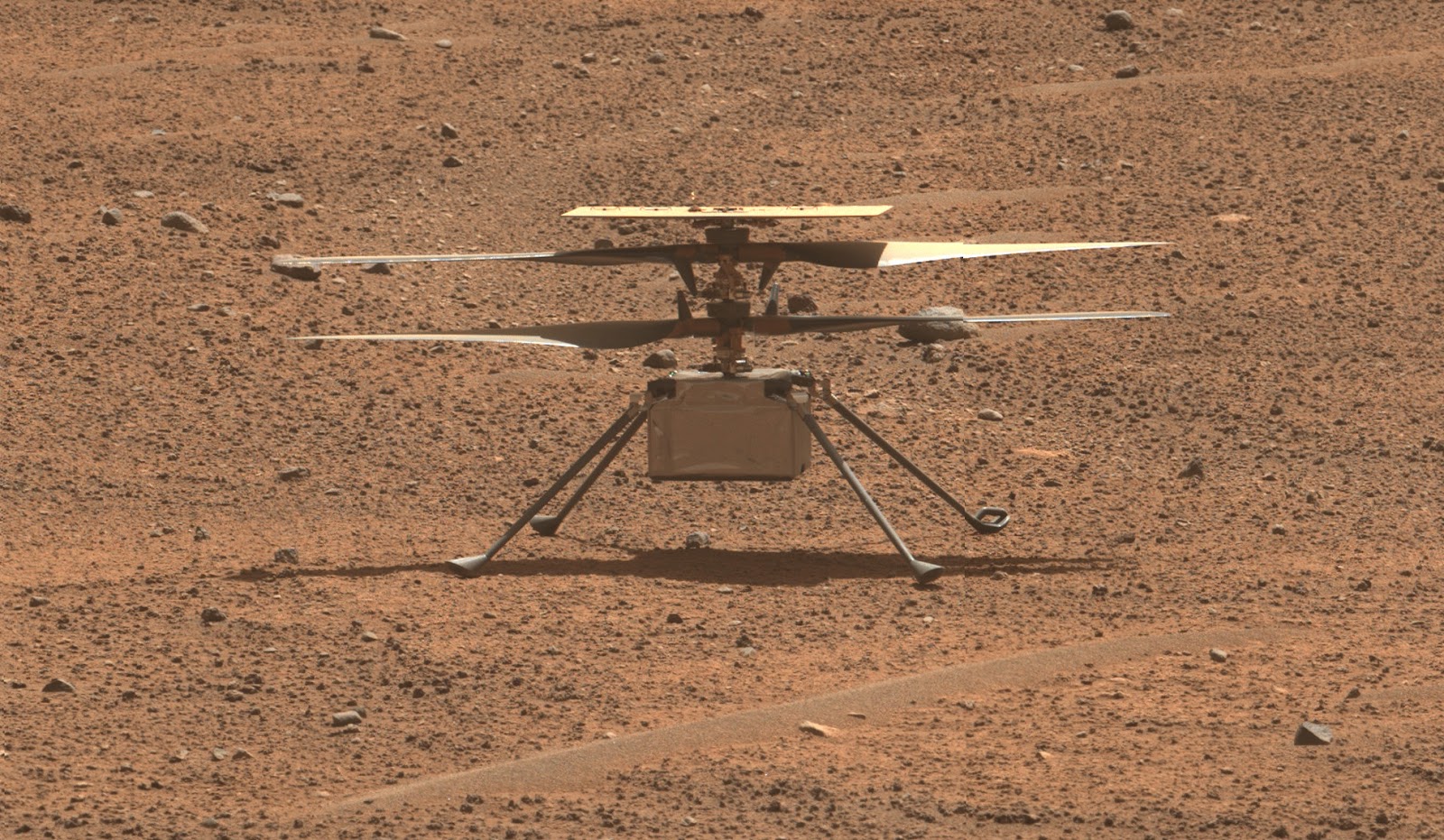


Ingenuity makes its final flight
In April 2021, two months after landing on the surface of Mars, NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter flew 10 feet into the air, hovered for 30 seconds, and then landed — earning a place in history as the first spacecraft to fly on another planet.
At the time, NASA expected to fly Ingenuity about four more times over the course of its 30 day mission. Instead, it has flown the tiny chopper a total of 72 times over the past 3 years, with Ingenuity racking up more than 2 hours in the air and traveling 14 times farther than anticipated.
Unfortunately, the overachieving helicopter sustained damage to one of its rotors during a recent flight, and on January 25, NASA announced that its mission has come to an end.
“History’s first Mars helicopter will leave behind an indelible mark on the future of space exploration and will inspire fleets of aircraft on Mars — and other worlds — for decades to come,” said Teddy Tzanetos, Ingenuity’s project manager at NASA.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].