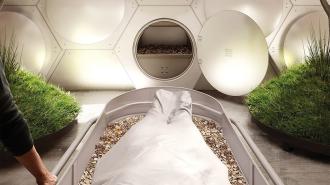
A newly signed bill makes human composting legal in California. Residents can now opt to have their bodies turned into nutrient-dense soil after their deaths, rather than being buried or cremated.
Circle of life: Human composting, also known as “terramation” or “natural organic reduction” (NOR), starts with the placement of a body in a sealed vessel along with organic materials, such as straw, flowers, and wood chips.
Air is circulated through the vessel, and microbes in the body begin the process of breaking down the human remains and plant material. About 30 to 60 days later, the vessel will contain roughly one cubic yard of soil.
After resting in a “curing bin” for a few weeks, the soil can be returned to the deceased’s loved ones, who might use it to fertilize a memorial garden or flower bed, or donated to an ecosystem restoration project.
“It seems like a peaceful way for the body to move on to the next phase.”
Charlotte Bontrager
The allure: Some people are drawn to human composting because they believe it’s a more natural, graceful alternative to burial or cremation.
“[Y]ou’re not being burned up, not being pumped full of embalming chemicals and taking up space in a container,” Charlotte Bontrager, whose mother Paulie Bontrager requested and underwent terramation in Washington state, told the Seattle Times in 2021.
“It seems like a peaceful way for the body to move on to the next phase,” she continued.
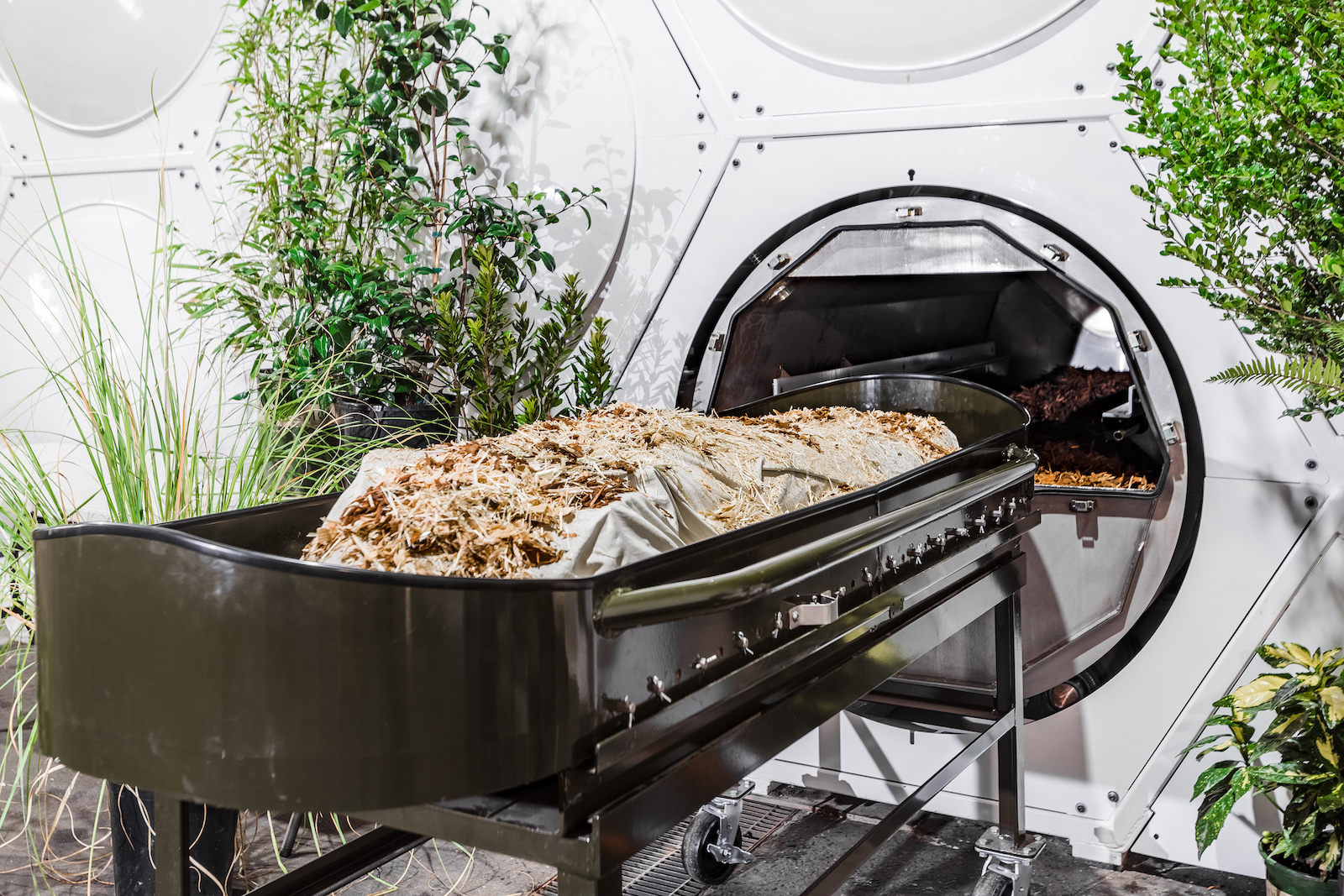

Many others, including Cristina Garcia, the lawmaker who drafted California’s human composting bill, advocate for terramation because it’s more environmentally friendly than traditional deathcare options.
“This is an alternative method of final disposition that won’t contribute emissions into our atmosphere and will actually capture CO2 in our soil and trees,” said Garcia. “For each individual who chooses NOR over conventional burial or cremation, the process saves the equivalent of one metric ton of carbon from entering the environment.”
“Climate change, the state of the planet, the grief we feel about it, is making people more conscious of their end of life, their impact on the planet.”
Katrina Spade
The big picture: Even so, human composting is only just becoming an option in the US — prior to 2019, when Washington became the first state to explicitly allow terramation, the only legal ways to dispose of human remains were burial, cremation, or donation.
Colorado, Oregon, and Vermont have since made human composting legal, and California’s new law requires officials to develop regulations for it no later than 2027. Advocates are hopeful it won’t be long before everyone has access to the eco-friendly deathcare option.
“Climate change, the state of the planet, the grief we feel about it, is making people more conscious of their end of life, their impact on the planet,” Katrina Spade, founder and CEO of human composting company Recompose, told NBC News.
“Human composting can be the next cremation,” she continued. “If we can really be the default, it would make a tremendous impact.”
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].