Researchers have finally hacked into the largest brain of all invertebrates — the squid. This work, creating the first gene-edited squid, smooths the way for advancing research on neurodegenerative diseases like Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s, or Parkinson’s.
As strange as it sounds, squid brains could teach us about human brain health. Squids have huge, well-developed brains, and they can perform some astonishing parlor tricks. They can change color spontaneously, tweak their genetic code, and swim backward.
Researchers use these intelligent creatures to study the nervous system, and they use the squid’s big thinker in brain research. One 1950s’ study on squid helped researchers discover the nerve impulse — a discovery that made Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley Nobel laureates in 1963. Nerve impulses are how neurons communicate with each other. It is the physiological foundation for neuroscience research. Squid have been riding shotgun in foundational neurobiology advances for decades.
Now, for the first time in history, scientists have used CRISPR, the DNA editing tool, to modify a squid. A gene-edited squid is a significant accomplishment that could push the sleek creatures to the forefront of genetic research — along with zebrafish and fruit flies.
Because squid are so intelligent and so complex, they could offer great insights on the role of genes on behavior.
“They’ve evolved these big brains and this behavioral sophistication completely independently (of humans),” scientist Joshua Rosenthal told NPR. “This provides an opportunity to compare them with us and see what elements are in common, and what elements are unique.”
For a long time, the squid’s physical makeup hasn’t made it easy for researchers to access their embryos for editing — and it isn’t because they are slippery. Squid embryos have a tough outer layer, which is hard to safely open up.
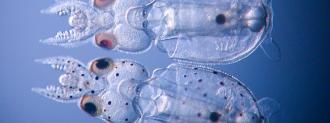
But researchers at Marine Biological Laboratory found a way in using micro-scissors and a quartz needle. Once they were in, scientists Joshua Rosenthal and Karen Crawford, used CRISPR-Cas9 to “knock out” a pigmentation gene — essentially turning off the color in the gene-edited squid’s specialized skin cells. These squids typically have black spots on their body, but the gene-edited squids were transparent.
“This is a critical first step toward the ability to knock out — and knock in — genes in cephalopods to address a host of biological questions,” said Rosenthal, who published the breakthrough study in Current Biology.
In comparative genomics, scientists perform studies on animals — like removing or “knocking out” a gene — that they can’t do on humans. Then they relate the results to humans by comparing their genomes.
Researchers will use the knock out technique to study gene function and genetic mutations, allowing researchers to test the role that many human genes play in squids. (Despite our distant ancestry, humans and squid do share many genes, such as those used to make eyes.)
“Now we actually have the ability to go in and test what an individual gene does,” MBL marine biologist Carrie Albertin told NPR. “This is something that honestly, if you asked me five years ago if we’d be able to do, I would have just giggled and said, ‘I dream of it’. But, you know, I didn’t think it would be possible. And yet here we are.”