Biotech
Human history has been all but defined by death and disease, plague and pandemic. Advancements in 20th century medicine changed all of that. Now advancements in 21st century medicine promise to go even further. Could we bring about an end to disease? Reverse aging? Give hearing to the deaf and sight to the blind? The answer may be yes. And soon.
More
New research on deep brain stimulation shows biomarkers could help depression treatment
Deep brain stimulation can alleviate treatment-resistant depression for some patients, and could help doctors measure outcomes.
Why aren’t we moving faster on malaria vaccines?
COVID-19 shots were rolled out within weeks of approval. The malaria jab is being delayed until mid-2024. Why?
What the science really says about vitamin D deficiency
When is low vitamin D a potential concern? And when might you need to get your levels tested? Here’s what the evidence says.
Why this startup is creating edible oil from sawdust
ÄIO’s main goal is to replace palm oil with oil upcycled from low-value industry organics in order to prevent further deforestation.
MIT study shows AI conversations are more positive if users think AI is empathetic, negative if they think it’s nefarious
Study shows users can be primed to believe certain things about an AI chatbot’s motives, which influences their interactions with it.
Stanford plans to put a 3D-printed human heart in a pig by 2028
Using 3D bioprinting, scientists are trying to construct perfect replacements for damaged organs, bones, and tissues.
Ever wonder how your body turns food into fuel? We tracked atoms to find out
New research offers new way to understand our metabolism in unprecedented detail, identifying four distinct phases of the process.
Monkey lives with CRISPR’d pig kidney for over two years
A monkey that survived for 758 days with a kidney from a gene-edited pig is a major step forward for xenotransplantation research.
CRISPR protects 9 out of 10 chickens from bird flu
UK scientists have used CRISPR to create gene-edited chickens that are highly resistant to the avian flu virus.
What does the evidence say about omega-3 fats for heart disease, dementia, and arthritis?
Are fish oil supplements as good for preventing heart disease, dementia, and other health conditions as we think? Or is eating fish better?
New superbug vaccine turns the immune system into “the Hulk”
A superbug vaccine that temporarily puts the immune system on high alert could reduce the number of hospital-associated infections.
After studying 850 hours of footage, this paper offers 3 rules for a great conversation
Good conversations leave a lasting impression. They are rewarding and enriching. Here’s how to have more of them.
Where are the universal coronavirus vaccines?
Universal coronavirus vaccines that protect against all known variants of COVID-19 — and ones that don’t exist yet — are closer than ever.
Study finds exactly how long people want to live: it isn’t forever
Most people prefer a shorter life if they have dementia, chronic pain, or are a burden to their families.
New “Lattice” device tests drugs on eight organs at once
Northwestern University scientists have developed a device that simulates up to eight organs at once to aid drug development.
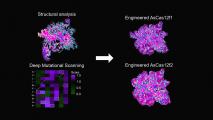
New CRISPR system is 66% smaller but just as powerful
A new CRISPR system is just as efficient as CRISPR-Cas9 but much smaller, which could make it easier to deploy in people.
These earbuds analyze brain activity and sweat content
A flexible sensor turns a pair of earbuds into a health monitoring device capable of recording brain activity and analyzing sweat.
Jellyfish surprise scientists by learning without a brain
Researchers demonstrate that Caribbean box jellyfish don’t just float around aimlessly. They learn and adapt to their environment.
Is iron the Achilles’ heel for cancer?
Some cancer cells store high quantities of iron. Iron-activated cancer drugs selectively disrupt cancer cells, without harming healthy cells.
Adding spider DNA to silkworms creates silk stronger than Kevlar
Spider silk is strong and tough, but hard to farm. Silkworm silk is easy to farm, but not that strong. What if we could combine the two?
Get inspired with the most innovative stories shaping the world around us.