Biotech
Human history has been all but defined by death and disease, plague and pandemic. Advancements in 20th century medicine changed all of that. Now advancements in 21st century medicine promise to go even further. Could we bring about an end to disease? Reverse aging? Give hearing to the deaf and sight to the blind? The answer may be yes. And soon.
More
Your moral compass could be broken
If we can better understand the evolution of our moral compass, psychologists believe we can begin working toward a society built on empathy over judgement.
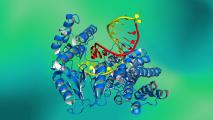
DeepMind AI cracks the code of protein structures
A protein’s structure is crucial to its function. Predicting how a protein will fold was a challenge decades in the making — and answered by DeepMind.
CRISPR used to edit HIV cure into monkey embryos
A mutation of the CCR5 gene can cure HIV — and thanks to CRISPR, scientists may soon be able to study it in animal models.
The quest for a “warm” COVID-19 vaccine
Developers are on the hunt for a warm COVID-19 vaccine, one that could be distributed in places where a reliable cold chain isn’t available.
This databank of mammalian genomes is the Noah’s Ark of DNA
The Zoonomia Project is the largest database of mammalian genomes to date, and it’s already helping researchers study SARS-CoV-2 and extinction risk.
Congo just used vaccines to beat Ebola. What they learned could stop COVID, too.
Congo’s recent success delivering frigid Ebola vaccines to remote areas may provide invaluable experience for a COVID-19 vaccine cold chain.
Cancer immunotherapy “baits” the immune system into attacking hidden lung tumors
When cancer spreads, it often ends up in the lungs. ImmunoBait can ride a red blood cell in mice to deliver cancer immunotherapy where they live.
We can now see a virus invasion in real-time
Understanding how a virus infects and replicates in a cell is crucial to stopping them. Now, researchers can see an infection in real-time.
The hep C cure may also fight COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 uses a number of key proteins to infect us, including its main protease. New research has found hepatitis C drugs can bind this protein.
Stopping nightmare disorder with a prescription-only watch
A prescription-only watch that treats nightmare disorder is the latest in a growing subset of health technologies called prescription digital therapeutics.
CRISPR could help save coral reefs from bleaching
Using CRISPR, scientists have identified a gene that could determine whether coral reefs are highly susceptible to bleaching or not.
When will we have a COVID-19 vaccine?
Several developers have reported incredible coronavirus vaccine progress, so when will we have a COVID-19 vaccine ready for distribution?
Reverse engineering a $15k medical device for 50x less
Many hospitals in developing countries can’t access the overpriced, high-tech equipment that’s standard in the U.S. Reverse innovation could finally change that.
Oxford says its COVID-19 vaccine is up to 90% effective
The University of Oxford’s COVID-19 vaccine was up to 90% effective in a phase 3 trial and could be easier to distribute than other coronavirus vaccines.
How long will coronavirus immunity last?
Coronavirus immunity might last for years, according to a new study that measured the levels of virus-fighting immune cells in COVID-19 survivors.
New skin cancer vaccine is twice as powerful
By adding two “boosters” to an in-development skin cancer vaccine, scientists may have improved its ability to prevent melanoma recurrence.
Do apologies even matter?
Science is finally proving that the act of apologizing can save and strengthen a relationship that’s been damaged by conflict.
Bacteria could make space mining 400% more efficient
Using a bioreactor packed with bacteria could make space mining more efficient by speeding up the extraction of elements from rock.
New vanishing wound dressing heals skin with minimal scarring
A new kind of hydrogel dressing improves wound healing and minimizes scarring by kicking the adaptive immune system into gear.
FDA authorizes first at-home COVID-19 test
The FDA has authorized an at-home COVID-19 test that delivers results in 30 minutes, but you can’t get it without a prescription.
Get inspired with the most innovative stories shaping the world around us.