Biotech
Human history has been all but defined by death and disease, plague and pandemic. Advancements in 20th century medicine changed all of that. Now advancements in 21st century medicine promise to go even further. Could we bring about an end to disease? Reverse aging? Give hearing to the deaf and sight to the blind? The answer may be yes. And soon.
More
New ALS treatment appears to slow disease progression
A new ALS treatment that appears to slow disease progression offers hope to those battling the incurable neurological disorder.
Weird, synthetic intestinal lining could make treating diseases easier
A synthetic intestinal lining could make it easier for doctors to control drug delivery and nutrient absorption in patients.
FDA approves first artificial pancreas for young children
The FDA has approved a new artificial pancreas for children, making diabetes management easier for caretakers of diabetics as young as two.
What we know about COVID-19 reinfection so far
Researchers have reported four cases of COVID-19 reinfection, with patients recovering from the coronavirus and later testing positive for another strain.
“Extinct” New Guinea singing dog is found again, thanks to genetics
The New Guinea singing dog was considered extinct in the wild. But, new genetic evidence suggests otherwise.
Microdosing LSD may provide pain relief
Since the 1960s, LSD has been seen as a potential painkiller. Now, new research suggests microdosing LSD may indeed provide relief.
Robots are running COVID-19 drug development
IBM’s new online platform, RoboRXN, combines artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and robotics to automate the COVID-19 drug development process.
It's now easier to see individual atoms, thanks to new tech
With improved tech, two teams have sharpened cryo-electron microscopy to be able to see individual atoms.
A patient’s sex may affect their COVID-19 immune response
Key differences in the COVID-19 immune response of men and women could potentially explain a disparity in patient outcomes.
Influenza virus may be transmitted by particles in the air
Airborne particles like dust and dander not caused by breathing — “aerosolized fomites” — may be a route of influenza virus transmission.
Did life on Earth travel here from Mars?
Bacteria that survived on the outside of the ISS for three years suggests that panspermia is still a viable theory for the origin of life on Earth.
The social distancing traffic light
Assessing your COVID-19 risk for everyday activities will be key to some kind of normalcy. Now, researchers want to add nuance to social distancing.
Elon Musk: Neuralink brain implant detects pigs' movements
During a livestream, CEO Elon Musk presented the latest Neuralink brain implant, as well as what he claimed were several pig recipients of the device.
Teens create website to combat social isolation in seniors
To help combat the problem of social isolation, three Texas teens created Big & Mini, a website that sets up video chats between seniors and younger people.
$5 COVID-19 test could be a game changer in the US
Abbott Laboratories’ $5 COVID-19 test has secured an FDA authorization, meaning the U.S. now has access to a fast, accurate antigen test.
Redesigned syringe could increase global access to medicine
A double-barrel syringe developed at MIT makes it possible to inject highly viscous biologics, making them more accessible to patients.
A health app could someday detect heart disease via selfies
Researchers in Beijing created a new deep learning algorithm, which claims to detect signs of heart disease in the human face.
“Antivitamins” could be the cure for antibiotic resistance
The B1 antivitamin helps bacteria kill competing bacteria, leading researchers to suspect it could help us fight antibiotic resistance and superbugs.
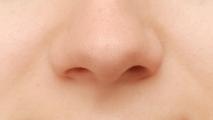
Why COVID-19 patients lose their sense of smell
Researchers have identified cells that are most susceptible to the novel coronavirus. They also support neurons associated with the sense of smell.
The murder hornet’s genome may help stop the invasion
The Asian giant hornet has invaded the Pacific Northwest. Researchers hope a map of the murder hornet’s genome can help their hunt for them.
Get inspired with the most innovative stories shaping the world around us.