Field: Brain
Living longer — and healthier — starts with boosting your brain
Science is beginning to unravel the reasons behind age-related cognitive decline — and what we can do about it.
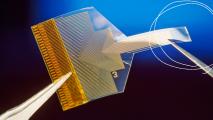
Flexible brain implant takes major leap forward
The FDA’s clearance of Precision Neuroscience's flexible electrode array pushes the startup ahead in the race to BCI commercialization.
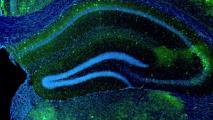
What hybrid mouse/rat brains are showing us about the mind
Modified mice with hybrid brains that include rat neurons could one day lead to new breakthroughs in neuroscience.
How sensory gamma rhythm stimulation clears amyloid in Alzheimer’s mice
Study finds stimulating a brain rhythm with light and sound increases peptide release from interneurons, possibly slowing Alzheimer's progression.
Brain implant for “artificial vision” is still working after 2 years
A new type of brain implant technology has given a man with total blindness a kind of “artificial vision.”
In a future with brain-computer interfaces like Elon Musk’s Neuralink, we may need to rethink freedom of thought
In a future with more "mind reading," thanks to computer-brain interfaces, we may need to rethink freedom of thought.
“Universal” BCI lets anyone play games with their minds
A specially trained “decoder” slashes the time it takes a brain-computer interface (BCI) to read a user’s mind.
First person with a Neuralink brain implant reveals how he uses it
Elon Musk’s Neuralink has revealed the identity of the first person to receive its brain implant — and the man says it has changed his life.
How scientists are using sound waves to hack the brain
Korean researchers have developed a new form of ultrasound brain stimulation that could help the brain form new connections.
Evidence that gamma rhythm stimulation can treat neurological disorders is emerging
Researchers survey the therapeutic potential of noninvasive sensory, electrical, or magnetic stimulation of gamma brain rhythms.
Injections of brain protein reverse memory loss in mice
A protein called “KIBRA” could be the key to new Alzheimer’s treatments that don’t just slow disease progression, but reverse memory loss.
Scientists create the first “functional” 3D-printed mini brains
The first 3D-printed brain organoids that function like natural brain tissue could lead to breakthroughs in neuroscience.
Elon Musk’s Neuralink has implanted its first device in a human being
Now that Neuralink has implanted a device in a person, CEO Elon Musk is closer to his goal of making brain chips common in the future.
Tech hacks the nervous system to bring touch to virtual reality
Afference's Phantom conducts electrical signals through nerves in the fingers to convince your brain it feels objects in virtual spaces.
Three ways your environment affects your intelligence
These examples underscore the importance of environmental regulation and policies; otherwise, we might just be throwing away our intelligence.
This “supermaterial” created a transparent brain implant
An AI-powered transparent brain implant made of the supermaterial graphene can predict activity below the brain’s surface.
Psychoactive drug ibogaine helps veterans with TBI
A small study found that one dose of ibogaine could reduce the symptoms of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) for military vets.
Bioengineered protein could enhance memory
Memory-related conditions are notoriously hard to treat, but there may be a way to boost recall in the brain.
Does caffeine harm your decision-making?
A small study showed caffeine lessens decision-making. While preliminary, it raises questions about caffeine affects our "higher" cognitive functions.
Deep neural networks show promise as models of human hearing
In the largest study yet of deep neural networks trained to perform auditory tasks, researchers found surprising similarities to human hearing.
Neurosoft CEO says new brain implant is “basically 1,000 times softer” than anything on the market
Swiss startup Neurosoft’s flexible brain implant could give us a better way to analyze and stimulate the brain.
Bad sleep worsens pain. Researchers may have discovered why.
Inadequate sleep worsens pain, which makes it difficult to sleep. This cycle may stem from disruptions to the body's endocannabinoid system.
Zapping injured brains can improve cognition and memory
The lasting symptoms of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be treated with deep brain stimulation, according to a first-of-its kind trial.
Cholesterol drug suggests new way to treat Alzheimer’s
A cholesterol drug that reduced brain damage in mice could reveal a new approach to treating Alzheimer’s disease in people.
New brain decoder system offers hope for communicating by thought alone
Is this another step towards telepathy?
A new machine is able to keep the brain alive without a heart
A new device that lets scientists precisely control the brain's blood supply could lead to new neuroscience breakthroughs.
Memory champion explains how she memorizes 1,080 numbers in 30 minutes
Katie Kermode — a memory athlete with four world records — tells Big Think about her unique spin on an ancient technique to memorize unfathomably long lists of information.
New brain implant for depression tested in people for the first time
A tiny brain implant designed for at-home neurostimulation has been demonstrated in people for the first time.
New research on deep brain stimulation shows biomarkers could help depression treatment
Deep brain stimulation can alleviate treatment-resistant depression for some patients, and could help doctors measure outcomes.
Jellyfish surprise scientists by learning without a brain
Researchers demonstrate that Caribbean box jellyfish don't just float around aimlessly. They learn and adapt to their environment.
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer’s models
A potential new Alzheimer’s drug represses the harmful inflammatory response of the brain’s immune cells, improving cognition in tests.
Brain implant lets cancer patients try 20 different drugs at a time
A microdevice that injects up to 20 drugs into gliomas at once could help doctors quickly identify the best treatment for cancer patients.
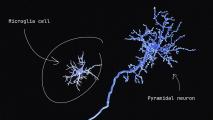
Scientists discover a new kind of brain cell
A newly discovered brain cell that appears to be a hybrid of the two other primary types could shake up the world of neuroscience.
Paralyzed woman able to speak again, thanks to brain-avatar interface
Speech BCIs that use brain implants and algorithms to translate brain signals into text are changing the lives of people with paralysis.
A Pink Floyd song was reconstructed from listeners’ brain waves
Training an AI to reconstruct a song from listeners’ brain activity revealed insights about the brain that could lead to better speech BCIs.
Brain scans reveal the mystery of “hidden consciousness”
Newly identified patterns of injury linked to “hidden consciousness” could lead to better outcomes for people in comas or vegetative states.
Mental illnesses affect brain structure, but in surprisingly different ways
A new brain mapping study identified commonalities in the brains of people with mental illnesses, and it could lead to better treatments.
Brain stimulation helps people with Parkinson’s walk
A noninvasive form of brain stimulation developed by Japanese researchers improved the symptoms of Parkinsonian gait in a small trial.
This unique human brain structure may have given us speech
Speech is unique to humans, yet most brain structures involved in speech are also present in Old World monkeys and other primates — except this one.
Study finds tracking brain waves could reduce post-op complications
Researchers found brain wave signatures that could help determine when patients are transitioning into a deep state of unconsciousness.
AI-powered brain implant restores feeling, movement in man with paralysis
A first-of-its-kind AI-powered brain implant has restored movement and feeling in a New York man with quadriplegia since 2020.
Australian military is funding a computer chip merged with human brain cells
The Australian military is funding research into "organoid intelligence" that involves stimulating lab-grown mini-brains with electrodes.
Immune cells in the brain may reduce damage during seizures and promote recovery
Microglia perform many functions in the brain, and their role in seizures is unclear — a new study in mice aims to find out more.
Scientists monitored the brains of 4 dying patients. Here’s what they found
Researchers found a surge of neurophysiological activity in the dying human brain, including in regions associated with conscious processing.
Brain-computer interfaces could let soldiers control weapons with their thoughts
Brain-computer interfaces raise many ethical questions about how and whether they should be used for certain applications — including war.
Two CRISPR treatments for Alzheimer’s ace early studies
Two teams of researchers have used CRISPR to alter the genes of mice to alleviate signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
4 ways to promote neurogenesis in your brain
Research from the 1960s proves creating new neurons as adults is possible, and modern-day research explains how to promote it.
ADHD drugs could alleviate symptoms of Alzheimer’s
Scientists reviewed 40 years of clinical studies that assessed the effects of NA-targeting drugs, such as certain ADHD drugs, on Alzheimer’s.
Neuroscience research triggers revision of a leading theory of consciousness
A brain scanning study on unconsciously processed visual information disrupts a leading theory of consciousness: global workspace theory.
Could switching off a neural “death response” slow aging?
A sensory mechanism that governs how quickly flies age may also have a corollary in people.
Neuralink’s monkey can play Pong with its mind. Elon Musk says human trials are next.
If Neuralink’s monkey can play Pong with its mind, imagine what humans could do with the same technology in just a few years.
Generate brilliant ideas by relaxing your cognitive filters
Theoretical physicist Leonard Mlodinow offers three strategies for relaxing your cognitive filters to give your brilliant ideas time to shine.
Cancer med appears to prevent brain aneurysms
Japanese researchers have discovered that the cancer drug sunitinib can prevent the formation of brain aneurysms in mice.
Have we got the brain all wrong? Study shows its shape is more important than its wiring
Neural activity may be more influenced by the shape of the brain – its grooves, contours, and folds – than by its complex interconnections.
Flexible brain implant tested in people for the first time
Startup Precision Neuroscience has tested its flexible, ultra-thin brain implants in people for the first time.
Rhythmic brain stimulation could boost cognitive function
An analysis of over 100 studies helps resolve conflicting evidence on the benefits of transcranial alternating current stimulation, or tACS.
Ketamine is as effective as ECT for depression, study shows
A trial of patients with treatment-resistant depression found ketamine to be at least as effective as electroconvulsive therapy.
Zapping the brain during sleep helps memories form
Brain stimulation during sleep appears to help with memory consolidation, suggesting a new way to treat people with memory disorders.
Do we finally know what causes Alzheimer’s?
The first treatments proven to slow cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s are helping settle a decades-long debate about how the disease starts.
Paralyzed man walks again using only his thoughts
A man with paralyzed legs is walking again thanks to a “digital bridge” between his brain and a spinal stimulator.
Depression treatment reverses “backwards” brain signals
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) appears to relieve depression by correcting brain signals that are traveling the wrong direction.
This soft brain implant unfurls its arms under the skull
A soft brain implant that unfurls under the skull could make implantation surgeries less costly and risky.
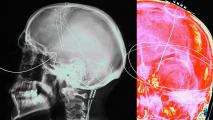
First-in-US brain surgery performed in Boston
A surgical team has performed a surgery that alleviated a dangerous brain condition before it was too late.
Amish gene study finds clues to mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder
Researchers have turned to this unique genetic population to find insights into how our genes play a role in mental health.
Complex brain activity detected in dying patients
Researchers have measured gamma waves, a sign of brain activity, in patients who were dying.
New Alzheimer’s drug slows cognitive decline by 35%
Eli Lilly’s new Alzheimer’s drug, donanemab, slowed cognitive decline by 35% in a phase 3 trial, but two people died from side effects.
Networks of silver nanowires seem to learn and remember, much like our brains
Self-organising networks of tiny silver wires appear to learn and remember in much the same way as the thinking hardware in our heads.
Scientists discover “anxiety gene” in the brain — and a natural way to turn it off
The discovery of an "anxiety gene" — and a natural way to put the brakes on it — in mice could lead to new treatments for anxiety disorders.
New gel destroys brain cancer in 100% of treated mice
A new brain cancer treatment not only cured 100% of mice that received it, but also trained their immune systems to fight future cancers.
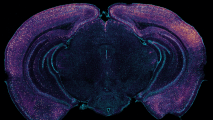
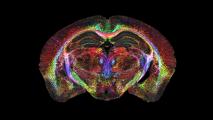
This brain image is 64 million times sharper than standard MRI
A new brain imaging technique that generates ultra-high resolution images of mouse brains could revolutionize neuroscience research.
LSD effective as major depression therapy in phase 2 trial
MindMed and University Hospital Basel have announced top line results for their phase 2 trial.
Graphene sensor could let you control robots with your mind
The “wonder material” graphene has been used to develop a dry sensor that could enable anyone to control technology with their minds.
Death: how long are we conscious for and does life really flash before our eyes?
When does our consciousness disappear? And are we really flooded by memories in our final moments? Scientists hope to find out.
How close are we to reversing paralysis?
Thanks to groundbreaking innovations in neuroscience, we’re seeing that forms of paralysis long assumed to be permanent can be reversed.
Our new brains: neurotechnology advances that could change everything
Here are the latest developments in neurotech, from brain-computer interfaces to brain-inspired AI.
3D-printing the brain’s blood vessels with silicone could personalize neurosurgery
3D printing could make blood vessel replicas with the soft feel and the structural accuracy surgeons need.
Have scientists found a “brake pedal” for aging?
A new protein discovery may have highlighted a "switch" in brain cells that slows down inflammation and aging.
Wristband device helps to control Tourette’s tics in clinical trial
A new wrist-worn device from the University of Nottingham uses electrical pulses to help curb Tourette syndrome symptoms.
Pfizer’s nasal spray for migraines is heading to pharmacies
The FDA has approved Pfizer’s zavegepant, a nasal spray for migraines that can ease pain in as few as 15 minutes.
“Digital detoxes” don’t work. Try these 4 skills instead
Digital distractions have become a ubiquitous part of work and life. But these distractions begin with emotional discomfort.
Breakthrough study discovers that psychedelics breach our neurons
Researchers have discovered that psychedelics can activate 5-HT2A receptors inside of cortical neurons, a possible cause of their therapeutic effects.
Psychedelics are helping dying patients overcome their existential distress
End of life patients face existential and spiritual challenges other patients do not. Psychedelics may be uniquely suited to helping them.
First: Spinal cord stimulation helps stroke survivors control arms again
Spinal cord stimulation has been shown to improve upper-limb mobility in stroke survivors for the first time.
DMT therapy appears effective for depression in phase 2 clinical trial
London-based Small Pharma has released positive top-line results for their phase 2a trial of DMT as an antidepressant.
Human-rat brain hybrid shows a way to cure blindness
New research has shown that human “mini brains” can integrate with damaged rat brains to perform functions related to sight.
New brain implant breaks record for turning thoughts into text
Stanford researchers have developed a brain-computer interface that allowed a woman to “type” 62 words per minute using only her thoughts.
New biomarker test accurately predicts who will respond to antidepressant
Alto Neuroscience’s depression drug seems effective in early trials, a proof-of-concept for biomarker-based design.
Brain experiment suggests that consciousness relies on quantum entanglement
Researchers possibly witnessed entanglement in the brain, indicating that some brain activity, like consciousness, operates on a quantum level.
New brain cancer treatment trialed in children for the first time
MRI-guided focused ultrasound has been used to deliver chemo into the brain of a pediatric cancer patient for the first time.
“Jumping genes”: A new model of Alzheimer’s
A new hypothesis suggests that Alzheimer's disease is the result of "jumping genes" in the brain, not inflammation or plaque.
FDA approves new Alzheimer’s medication
Lecanemab, a new Alzheimer’s medication shown to slow cognitive decline in patients, has been granted accelerated approval by the FDA.
How to use the brain’s own immune cells to stave off Alzheimer’s
Research suggests that microglia play a key role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases by helping to remove toxic waste.
MIT is testing light and sound to combat Alzheimer’s
MIT researchers are developing a therapy that uses 40-Hz light and sound to alter Alzheimer’s patients’ gamma waves.
AI-based theory explains your weird dreams
Researchers suggest that dreaming helps us generalize our experiences so that we can adapt to new circumstances.
Magnets pull these tiny medical robots deep into the brain
LA-based startup Bionaut Labs is developing micro-sized medical robots that are guided through the body by magnets.
Watch a Neuralink robot insert electrodes into a dummy brain
During a livestreamed event, a Neuralink robot precisely inserted 64 electrode-packed threads into a dummy brain in just 15 minutes.
New brain cancer vaccine completes clinical trial
Northwest Biotherapeutics reports that its new brain cancer vaccine can extend glioblastoma patients’ lives by months or even years.
Study finds mindfulness as effective as medication for anxiety
An intensive form of mindfulness was found as effective as Lexapro in treating anxiety in adults in the first head-to-head comparative study.
New deep brain stimulator is powered automatically by breathing
A deep brain stimulator powered by breathing could eliminate the need for patients to undergo regular battery-change surgeries.