Field: Genetics
What is The Great Progression: 2025 to 2050?
We have a historic opportunity to harness AI and other transformative technologies in order to make a much better world in the next 25 years.
We’re able to create new creatures through gene editing. What’s stopping us?
The question isn’t whether we can sculpt new life. The question is what comes next.
This $400 genetic test could save your life
Nucleus Genomics' new whole genome sequencing and analysis service promises to reveal the secrets hidden in your DNA.
New study challenges long-held assumption about cancer
Genetic mutations may not be necessary for cancer to develop, challenging a long-held assumption about the disease.
How turning off one gene causes mice to grow 6 legs
A study of embryo development in mice led to the creation of a mutant mouse fetus with an extra pair of legs in place of genitals.
Soaring insulin costs? Cows could help.
A genetically engineered cow that produce milk containing with human insulin could help cut the cost of the life-saving diabetes med.
World’s first GM banana approved in Australia
Australian regulators have approved a GM banana modified to resist Panama Disease, a devastating fungal infection.
How our “junk DNA” led to humans being tailless
A CRISPR study out of NYU suggests that junk DNA likely led humans to evolve to be tailless millions of years ago.
Bioluminescent plants don’t exist in nature — but you can buy one for $29
Biotech firm Light Bio is selling gene-edited bioluminescent plants that glow green in the dark for just $29.
Netflix’s “You Are What You Eat” proves twin studies’ importance to science
What is it that makes twins so special, and how do researchers harness the power of twins? "You Are What You Eat" helps prove their importance.
One-shot CRISPR treatment for inherited disease aces first human trial
A CRISPR treatment for hereditary angioedema significantly reduced swelling attacks in its first human trial.
New DNA testing reveals who made ancient stone tools
Using modern DNA analysis techniques, archaeologists have solved the mystery of who made a class of ancient stone tools.
Deaf boy hears within days of receiving new gene therapy
A gene therapy designed to treat a rare form of genetic deafness has restored hearing in the first patient to receive it.
Bioengineers design a new plant to purify air faster than nature
Neoplants has bioengineered a pothos plant that removes 30 times more pollutants from the air than a regular houseplant.
How does Alzheimer’s disease erode memory? New findings on risk gene offer insights
The strongest genetic predictor of Alzheimer's disease is a variant of a gene called apolipoprotein E. Researchers are discovering why.
New on/off switch in mRNA lets doctors “tune” gene therapy
A new kind of mRNA switch could give doctors the ability to precisely control the expression of therapeutic genes.
Bioengineered protein could enhance memory
Memory-related conditions are notoriously hard to treat, but there may be a way to boost recall in the brain.
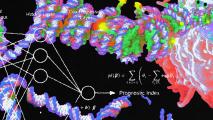
New AI predicts cancer survival using epigenetics
Researchers from the UCLA train an AI to use epigenetics to predict clinical outcomes for cancer patients.
Untangling the genetics that underlie our facial features
Hundreds, if not thousands, of genes affect the shape of the face, in subtle ways. Researchers explain why, and how, we look like our family.
Startup can now screen IVF embryos for 1000+ diseases
Startup Orchid now offers whole genome sequencing for embryos used during IVF — but not everyone is convinced it’s worth the cost.
Search algorithm reveals nearly 200 new kinds of CRISPR systems
Researchers have discovered rare new CRISPR systems that have a range of functions and could enable gene editing, diagnostics, and more.
New gene therapy reverses hearing loss in 4 children
A new gene therapy being trialed in China was able to reverse hearing loss in 4 of the 5 children to receive it.
Ex-NASA engineer Mark Rober created the world’s smallest Nerf gun — from DNA
Mark Rober and Pallav Kosuri created a Nerf gun so tiny they had to build it out of DNA. This DNA "origami" has the potential to revolutionize engineering.
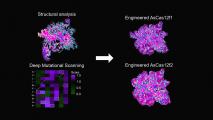
New CRISPR system is 66% smaller but just as powerful
A new CRISPR system is just as efficient as CRISPR-Cas9 but much smaller, which could make it easier to deploy in people.
Adding spider DNA to silkworms creates silk stronger than Kevlar
Spider silk is strong and tough, but hard to farm. Silkworm silk is easy to farm, but not that strong. What if we could combine the two?
Rare mutation may counteract “Alzheimer’s gene”
A rare mutation suggests that using CRISPR to reduce the expression of the APOE-e4 gene could help treat or prevent Alzheimer’s.
New CRISPR tool has an “on/off” switch
By splitting a base editor into two parts, researchers could give it an “on/off” switch that appears to make it safer and more effective.
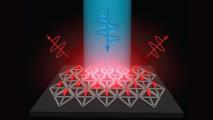
Arrays of quantum rods could enhance TVs or virtual reality devices
MIT engineers have used DNA origami scaffolds to create structured arrays of quantum rods, which could be incorporated into LEDs.
One-shot gene therapy for liver disorder works in a small trial
A new gene therapy for the rare liver disorder Crigler-Najjar syndrome was highly effective in a small trial.
Extreme treatment for alcoholism slashes drinking by 90% in monkeys
An in-development treatment for alcoholism dramatically reduced consumption in monkeys that previously drank heavily.
Fragile X syndrome often results from improperly processed genetic material
Researchers discovered that the mutated gene responsible for fragile X syndrome is active in most people with the disorder, not silenced.
New study shows how electricity can turn on genes
A prototype wearable demonstrates a novel way to trigger gene expression: by zapping cells with electricity.
First-of-their-kind eye drops reverse blindness in teen
A topical gene therapy designed to heal the wounds of people with “butterfly skin disease” has now been used to reverse blindness.
Got COVID but felt fine? It may be your genes.
A person’s chances of having asymptomatic COVID are dramatically increased if they possess a certain genetic mutation.
Aging is complicated – a biologist explains why no two people or cells age the same way
While some people may be older in chronological age, their biological age might be much younger. A biologist explains why.
Can we train our taste buds for health?
Reformulating foods tailored to the plasticity of our taste buds could be a practical and powerful tool to promote health.
First CRISPR-like system discovered in animals
A CRISPR-like gene-editing system found in animals and other complex organisms has been used to edit human cells for the first time.
“Backdoor” into the ear offers new hope for reversing deafness
A new study has unlocked a “backdoor” into the inner ear that could make administering gene therapies to restore hearing less risky.
“Spooky” quantum biology might cause your DNA to mutate
Research suggests that quantum effects could drive mutations in human DNA — the latest development in the emerging field of quantum biology.
The placenta may play a role in the genetic risk of schizophrenia
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have found that genes associated with schizophrenia risk may impact the placenta, not just the brain.
New kind of chicken lays eggs that don’t have allergy protein
Newly created gene-edited hens lay eggs without ovomucoid, the protein most likely to trigger an egg allergy.
We’re analysing DNA from ancient and modern humans to create a “family tree of everyone”
Genetic genealogy not only helps us understand where we came from, but it could also be used for tracing the origin of genetic mutations.
A banana that doesn’t go bad so fast approved by the Philippines
Billions of bananas are wasted every year, but that may change soon.
Man’s mutated gene appears to delay onset of Alzheimer’s
The discovery of a second person naturally resistant to a genetic form of Alzheimer’s could lead to treatments for the disease.
New gene therapy could reverse a common cause of blindness
A new study suggests we may be able to convert dormant eye cells into photoreceptors to reverse retinal degeneration.
Scientists treated heart attacks in mice — before they happened
By toggling an important heart gene, scientists have treated mice for a heart attack preemptively.
A new look at the strange case of the first gene-edited babies
Did He Jiankui "Make People Better"? A new documentary leans toward a different narrative about gene-editing than we've heard before.
This “living medicine” can eliminate a deadly lung infection
Researchers have engineered bacteria to create a “living medicine” against a nasty respiratory bug.
5 biotech trends to watch in 2023
After a monumental year of breakthroughs, scientists, investors, and CEOs share which areas of biotech they are eagerly watching this year.
Study finds 155 tiny new genes evolving in humans
Microproteins encoded in short strands of DNA reveal our recent evolutionary history, and hint at how human genetics may be changing.
“Jumping genes”: A new model of Alzheimer’s
A new hypothesis suggests that Alzheimer's disease is the result of "jumping genes" in the brain, not inflammation or plaque.
Resurrecting a 2.6 billion-year-old ancient CRISPR system
Researchers have resurrected an ancient CRISPR system 2.6 billion years old, capable of editing genes in the modern day.
A single injection of gene therapy made old mice live 7% longer
Biotech startup Rejuvenate Bio says it has extended the lives of elderly mice by 7% using a technique called “partial reprogramming.”
Mother’s mitochondria used to treat her child’s rare genetic disorder
A new therapy that treats children with rare mtDNA mutations using mitochondria sourced from their mothers has now been tested in patients.
Genetic research confirms your dog’s breed influences its personality — but so do you
A dog's breed has a big impact on their personality, but whether they fit your lifestyle is also down to good training.
New antibody therapy works for 73% of multiple myeloma patients
A new multiple myeloma therapy that uses an antibody to bring T cells to the cancer has shown efficacy in clinical trials.
Startup unveils $179 houseplant engineered to purify your air
Neoplants' $179 genetically engineered houseplant pulls VOCs from the air 30 times more efficiently than plants found in nature.
Deadly disease treated in the womb for the first time
In a medical first, doctors were able to prevent heart and muscle damage using enzyme replacement therapy.
$3.5 million treatment for hemophilia wins FDA approval
The FDA has approved biotech company CSL Behring's Hemgenix, a hemophilia B treatment that costs $3.5 million per dose.
Engineered bacteria may fight this brain-damaging genetic disorder
A possible phenylketonuria therapy using engineered bacteria has shown positive results in a small phase 2 trial.
Understanding cancer’s “dark matter”
Researchers have discovered that cancer’s epigenome — changes to how genes are expressed that aren’t mutations — may play a key role in its behavior.
What you eat can reprogram your genes
You are what you eat, and what your parents ate, and what their parents ate. An expert explains how the foods you eat can reprogram your genes.
UK scientists solve a decades-long blood mystery
Researchers have discovered a new blood group which may have been behind the tragic loss of two babies.
Like genes, your gut microbes pass from one generation to the next
Not only did microbes diversify with their early modern human hosts as they traveled across the globe, they followed human evolution.
Genetically engineered bacteria make living materials for self-repairing walls and cleaning up pollution
With just an incubator and some broth, researchers can grow reusable filters made of bacteria to clean up pollution and more.
A newly discovered class of RNA can fight off multiple viruses, including flu and SARS-CoV-2
Harvard-affiliated researchers have discovered a form of double-stranded RNA which may be a potent antiviral.
Shape-shifting DNA is helping researchers decode the human brain
Researcher Nako Nakatsuka has turned to DNA to tackle an important challenge: how do we measure chemicals in the brain?
World’s first cloned arctic wolf is now 100 days old
After two years of effort, China's Sinogene Biotechnology has created the world’s first cloned arctic wolf.
Identical twins were raised in different countries. Here’s how they differ today.
After being separated as toddlers, two identical twins were raised apart in the US and South Korea.
Woman with rare gene mutations feels no pain, anxiety
A woman in Scotland was found to feel virtually no pain and report zero trace of any anxiety or depression.
Breakthrough in photosynthesis boosts plant growth up to 30%
In a small study, researchers have engineered soy plants to have higher yields thanks to improved photosynthesis.
An international team sets out to cure genetic heart diseases with one shot
Researchers from the UK, US, and Singapore are beginning work on a genetic heart cure they hope to begin clinically testing within five years.
First personalized CRISPR therapy approved for trial
The FDA has approved a trial for the first personalized CRISPR therapy, which was developed to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Which microbes live in your gut? A microbiologist tries at-home test kits
A microbiologist looks at how home test kits work, what kind of information they provide and if they can really help change your gut.
Cells become zombies when the ends of their chromosomes are damaged
Damage to the ends of the chromosomes can create “zombie cells” that are still alive but can’t function, researchers say.
Transhumanism: Savior of humanity or false prophecy?
While many of the technologies upon which transhumanists base their dream are real and world-changing, they have major limitations.
How natural “short sleepers” thrive on 4 hours of sleep per night
Natural "short sleepers" thrive on only four to six hours of sleep per night. Could their genetics explain why?
Your genes may impact psychedelic experiences
UNC researchers have found evidence that the genetic makeup of a crucial receptor may impact your psychedelic experience.
Large study of 20,000 cats and dogs could help pets live longer
Mars Petcare has announced the opening of a massive biobank to study aging and pet diseases.
Potential cause of unexplained epilepsy cases uncovered
University of Arizona researchers have uncovered a protein that might be behind some epilepsy cases with currently unknown causes.
“Soft CRISPR” is safer and could help cure more diseases
A new CRISPR system was far more effective and precise than CRISPR-Cas9 when tested in fruit flies.
CRISPR cure for high cholesterol enters first human trial
A trial testing a new CRISPR-based treatment to lower cholesterol has officially kicked off in New Zealand.
An old HIV drug may treat Down syndrome
A common HIV drug could potentially be a Down syndrome treatment, improving cognition in mouse models of the condition.
Gene editing gone wrong: Scientists accidentally create angry hamsters
A team of scientists used gene editing to create what they thought would be a calmer rodent. Instead, the gene-edited rodents were angrier.
CRISPR cure for sickle cell nearly 100% effective after three years
A CRISPR therapy for sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia looks close to 100% effective three years after infusion.
A groundbreaking solution could unleash our hydrogen future
German researchers have created genetically engineered bacteria that can rapidly store and release hydrogen fuel.
New CRISPR-based map ties every human gene to its function
Researchers used a single-cell sequencing tool Perturb-seq on every expressed gene in the human genome, linking each to its job in the cell.
The age reversal tech that billionaires are banking on
How long can a human being not only live but thrive? A race to find out involves some of the biggest names (and bank accounts) in tech.
Gene therapy fixes rare heart disorder with clever workaround
Cleveland Clinic researchers have developed a gene therapy that cured arrhythmias in mice.
Chinese robot clones pigs with no human help
A robot that automates a common technique for animal cloning has been used to produce a litter of pigs in China.
A new treatment may cure neuropathic pain
A gene therapy tested in animals may be a safe, permanent, and non-addictive treatment for neuropathic pain in humans.
Genetic mutations can be benign or cancerous – here’s a new way to identify them
Identifying the difference between normal genetic variation and disease-causing mutations is vital for determining a person's treatment.
Gene editing could reverse anxiety and alcohol-use disorder
Gene editing may be a treatment for anxiety and alcoholism in adults who were exposed to binge-drinking in their adolescence.
How herpes wakes up
Researchers believe they have identified how herpes hiding in your cells wakes back up to cause symptoms.
Genes from over 5,000 stroke patients hint at surprising treatment
A study of nearly 6,000 stroke patient genomes suggests a treatment idea abandoned for decades should get a second look.
A Spanish teen’s genome may hold the secret to lupus
Researchers believe they have found a single point mutation in an infection-sensing gene that causes the autoimmune disorder.
How Robert Langer, a pioneer in delivering mRNA into the body, failed repeatedly but kept going
Langer published the first paper to show that it was possible to deliver nucleic acids like RNA and DNA to the body via tiny particles.
This wristband tells you what food to buy based on your DNA
By analyzing genetic code determining susceptibility to health conditions like diabetes, it tells you which foods are best for you.
An ancient enzyme could supercharge photosynthesis
Researchers have resurrected an ancient version of the enzyme Rubisco in the hope of supercharging photosynthesis in today’s plants.
Mutations in 16 species reveal clues to human aging
A surprising pattern in how often mammal cells undergo somatic mutations could be a boon to longevity research.