Field: Animals
How a dog’s life could extend yours
Studying animals — from long-lived clams to everyday dogs — is helping scientists understand aging and design therapies to slow decline.
Why the US has artificial reefs made from sunken ships and voting machines
Not all underwater reefs are made of coral − there are also artificial reefs made of sunken ships, radio towers, and more.
Cancer vaccine for dogs appears to nearly double survival rate
Yale researchers have developed a cancer vaccine for dogs that appears to increase their 12-month survival rate from 35% to 60%.
Anti-aging pill for senior dogs is now in clinical trials
An anti-aging pill for senior dogs now in clinical trials might lead to treatments that extend human lives, too.
Mice could someday become venomous, suggests study on the evolution of oral venom systems
Although scientists have a good understanding of the composition of snake venom, little is understood about the origins of venom systems.
First anti-aging drug for dogs nears approval
The FDA is a major step closer to approving biotech company Loyal's LOY-001, the first anti-aging drug for dogs.
Australia’s 30-year quest to unlock an ancient painkiller
A crocodile attack led to a 30-year partnership to develop a painkiller based on the Nyikina Mangala people's traditional knowledge.
Want to feel better? Science says to care for your dog
Research shows that caring for your pets can improve your well-being, and that the act of caring provided more improvements than mere companionship
Pigs proven intelligent enough to play video games
A quartet of porcine subjects at the Purdue Center for Animal Welfare Science learned to play a simple video game.
Do wolves harbor the secret to curing dogs’ bowel problems?
The problem with carnivores turned omnivores.
Sex life discovery raises IVF hope for endangered purple cauliflower soft coral
The purple cauliflower soft coral Dendronephthya australis, now listed as an endangered species, has a new hope of survival with IVF.
Monkey lives with CRISPR’d pig kidney for over two years
A monkey that survived for 758 days with a kidney from a gene-edited pig is a major step forward for xenotransplantation research.
Jellyfish surprise scientists by learning without a brain
Researchers demonstrate that Caribbean box jellyfish don't just float around aimlessly. They learn and adapt to their environment.
Adding spider DNA to silkworms creates silk stronger than Kevlar
Spider silk is strong and tough, but hard to farm. Silkworm silk is easy to farm, but not that strong. What if we could combine the two?
CRISPR is helping “de-extinct” the Tasmanian tiger
"De-extinction” researchers believe they might be able resurrect the Tasmanian tiger and restore ecological balance in Australia.
The underappreciated benefits of wild bees
The plight of wild bees has largely been overshadowed by concern about threats to domestic bees. Many people don't even know the difference.
Australian ant honey inhibits tough pathogens, new research shows
Honeypot ant honey may help develop our arsenal of effective antibacterial and antifungal treatments, which are increasingly vital.
Scientists bioengineer plants to have an animal-like immune system
Scientists have bioengineered a hybrid molecule by fusing components from an animal's and a plant's adaptive immune system.
A pig kidney is still working in a person after 32 days
A gene-edited pig kidney has been functioning in a person for a record-breaking 32 days and still shows no signs of failure.
Termite mounds inspire climate-friendly air conditioning
The intricate designs of termite mounds show how to maintain a comfortable climate, without using any power.
Lab-grown meat techniques aren’t new
Cell cultures are common tools in science, but bringing them up to scale to meet society’s demand for meat will require further development.
By 2040, 60% of “meat” won’t come from dead animals
"Novel vegan meat alternatives" and cultured meat will likely become competitors to traditional meat products, the report says.
Not all repellents are equal – here’s how to avoid mosquito bites this summer
Researchers studied different types of mosquito repellents and their efficacy for over a decade. Here's what they found.
“Zombie” cells are the key to a tiny sea creature’s full-body regeneration
A tiny sea creature’s regenerative abilities add to the growing evidence that senescent cells aren’t always detrimental.
Could switching off a neural “death response” slow aging?
A sensory mechanism that governs how quickly flies age may also have a corollary in people.
Farmers can fight invasive insects with AI and a robotic arm
As the invasive spotted lanternfly threatens to expand its range, Carnegie Mellon researchers are developing a robot to fight back.
A new organelle has been found in cells
Researchers have discovered a new organelle in the guts of fruit flies.
CRISPR sausage gets FDA green light for consumption
The FDA has given Washington State University researchers the green light to feed five gene-edited pigs to people.
New drug candidates found in an unlikely place
Costa Rica’s famed sloths harbor bacteria in their fur which can create antibiotic compounds — a potential source of future therapies.
Scientists figure out why tardigrades are nearly indestructible
Tardigrades have been frozen, boiled, exposed to extreme doses of radiation, and remarkably still survive. How?
Scientists train ants to sniff out cancer in just 30 minutes
Ants were just as accurate as cancer-sniffing dogs. Better yet, they could be trained in minutes rather than months.
Macaque monkeys shrink their social networks as they age — just like elderly people
Macaque monkeys reduce their social networks as they get older – research suggests evolutionary roots of the same pattern in elderly people.
Dog “nose print” app is 99% accurate at ID’ing lost pets
An AI-based app that identifies dogs and cats based on their unique nose prints could help reunite lost pets and their owners.
Bird flu is everywhere. Are the vaccines ready?
As avian influenza continues to devastate the bird population and jump into mammals, scientists are preparing to protect two important groups.
Mice grow mini deer antlers after stem cell transplant
The discovery of a new type of stem cell in deer antlers could lead to breakthroughs in human regeneration.
As bird flu spreads in the US and worldwide, what’s the risk that it could start a human pandemic?
Many virologists are concerned that the latest bird flu outbreak could spill over to humans and cause a new human pandemic.
Small wonders: The antibodies from camels and sharks that could change medicine
A handful of animals make a pared-down version of our own antibodies. Scientists hope to harness them as treatments for human illnesses.
New study discovers how to reverse hearing loss
A new study of hair cell regeneration in mice could help researchers figure out how to reverse hearing loss in people.
Strange life forms create an “alien” ecosystem in an abandoned uranium mine
Scientists have found diverse life forms dwelling in an abandoned, flooded uranium mine in Germany, creating an "alien" ecosystem.
“Bioprinted” skin could help end animal testing for cosmetics
Bioprinted skin can now look and act so much like real skin that it could one day replace some animal testing.
Google sister company aims to eradicate dengue from a tropical country
Verily, owned by Google parent company Alphabet, believes it can eliminate Singapore’s dengue problem.
Genetic research confirms your dog’s breed influences its personality — but so do you
A dog's breed has a big impact on their personality, but whether they fit your lifestyle is also down to good training.
Rewilding: letting nature do its own thing
Rewilding organisations in Europe are reintroducing lost species including the Eurasian lynx and Marsican brown bear.
Mega bacteria that can be seen with naked eye shakes up the field of microbiology
A newly discovered species of bacteria is so large that it can be seen with the naked eye. It also contains a DNA-containing nucleus.
Stem cell breakthrough could save the northern white rhino
To save the northern white rhino species from extinction, researchers are turning stored rhino tissue samples into sperm and egg cells.
Armadillo experiment suggests that we can regenerate human livers with leprosy
M. leprae-infected armadillos develop enlarged, healthy livers with gene expression patterns similar to human fetal livers.
New CRISPR tech makes it possible to wipe out invasive mice
Australian researchers have developed a gene drive that renders female mice infertile, opening the door to a new type of pest control.
Breakthrough drug cures sleeping sickness with one dose
A new, one-dose treatment for lethal sleeping sickness was 95% effective at clearing the parasite from patients.
Playing sea soundscapes can summon thousands of baby oysters – and help regrow oyster reefs
Researchers amplified the natural sounds of the sea through underwater speakers to draw baby oysters to swim to the location.
These psychedelic “body snatchers” regenerate their bodies and absorb other organism’s attributes
These bizarre mollusks have the ability to regenerate their bodies and to absorb other organisms' attributes.
Wild mammals are making a comeback in Europe thanks to conservation efforts
Many large mammals in Europe were close to extinction. New data shows us that the continent’s mammal populations are flourishing again.
Scientists discover slug that can decapitate itself, grow new body
Scientists observed two species of sea slug that were able to self-decapitate, survive for weeks without organs, and regenerate new bodies.
Why does nature create patterns?
A physicist explains the molecular-level processes behind crystals, stripes, and basalt columns in nature.
Sea turtles in Seychelles have recovered from the brink
The green turtles of Seychelles – once almost hunted to extinction – are now thriving again thanks to conservation efforts.
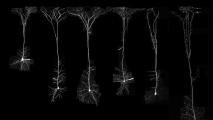
Study finds a striking difference between neurons of humans and other mammals
Researchers identified a “building plan” that holds true for every species they looked at — except for humans.
Scientists discover animal that doesn’t need oxygen to live
The parasite infects salmon and lives within the fish muscle, though scientists aren't quite sure how it breaks down nutrients for survival.
Axolotls can regenerate their brains
Axolotls are a model organism researchers use to study a variety of topics in biology because of their regenerative abilities.
World’s first cloned arctic wolf is now 100 days old
After two years of effort, China's Sinogene Biotechnology has created the world’s first cloned arctic wolf.
Dolphins use signature whistles to represent other dolphins – like names
Bottlenose dolphins are extremely social animals that communicate constantly, and consistently use signature whistles for one another.
Mouse embryos with beating hearts have been created entirely in the lab
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science have developed mouse embryos, complete with organ structures, purely from stem cells.
Great white sharks occasionally hunt in pairs
Think sharks are always solitary? New research sheds light on social behavior of these mysterious predators.
AI has mapped all of the world’s known ant species
Using over a million data points and a machine learning algorithm, a team of researchers has mapped all of the ant species currently known.
Eye implant made from pig skin reverses blindness in 14 people
Using collagen from pig skin, Swedish researchers created an artificial cornea that reversed blindness in 14 people.
Only human Lyme vaccine in development enters phase 3 trial
Pfizer and French biotech Valneva have announced a phase 3 clinical trial testing the human Lyme vaccine.
Yale team partially revives dead pig organs an hour after death
Yale’s OrganEx technology has been used to partially revive the organs of dead pigs an hour after their hearts stopped beating.
Crows are self-aware just like us, says new study
Crows and the rest of the corvid family keep turning out to be smarter and smarter. A corvid's pallium has more neurons than a great ape's.
Feeding insects to cattle could make meat and milk production more sustainable
Most U.S. adults aren’t ready to put insects on their plates but are much more willing to consume meat from livestock that are fed bugs.
Large study of 20,000 cats and dogs could help pets live longer
Mars Petcare has announced the opening of a massive biobank to study aging and pet diseases.
NYU performs two more pig-to-human heart transplants
Two pig-to-human heart transplants performed by surgeons at NYU Langone Health showed all the signs of success.
FDA may soon allow pig organ transplant trials
With pig transplantation looking increasingly viable, the FDA may soon allow clinical trials of the technique to begin.
A “Peter Pan” chemical could stop mosquitoes, without hurting other insects
Entomologist Naoki Yamanaka has an idea for how to handle mosquitoes: What if we just stop them from growing up?
Gene editing gone wrong: Scientists accidentally create angry hamsters
A team of scientists used gene editing to create what they thought would be a calmer rodent. Instead, the gene-edited rodents were angrier.
A dog cancer vaccine may save them and, one day, us
Dutch researchers have created a dog vaccine which may pave the way for similar human therapies.
Magic mushrooms evolved to scramble insect brains, send them on wild, scary trips
Researchers discovered that the way fungi independently gained the ability to produce psilocybin is because of horizontal gene transfer.
Three more nations eliminate sleeping sickness as a public health threat
Sleeping sickness is a horrifying disease mainly impacting the rural poor. But three more African nations have succeeded in curtailing its threat.
Ancient creatures inspire record-breaking new technology
Inspired by the ancient compound eyes of the trilobite, researchers have created a record-breaking camera with a depth of field of just over a mile.
The source of a strange anti-cancer compound is found in Florida
Researchers have discovered that common soft corals are the source of a sought-after anti-cancer compound.
Silkworms could one day repair human tendons stronger than before
Mixing silk protein with a gel matrix allowed for better cell growth and healing in rat models.
‘Mad honey’: The rare hallucinogen from the mountains of Nepal
On the mountainsides of Nepal and Turkey, bees sometimes produce a strange and dangerous concoction: mad honey.
Docs discover likely cause of pig heart transplant failure
A pig virus — and not organ rejection — appears to be the reason a man who lived for two months after a pig heart transplant ultimately died.
WWF report highlights tiger population gains for the Year of the Tiger
The global tiger population is finally increasing after more than a century of gradual decline, a new study from WWF reveals.
AI can now understand animal behavior
Animal behavior researchers can now turn the task of analyzing footage over to an open-source algorithm that can spot even subtle actions.
CRISPR could create hypoallergenic cats
The results of a recent study found that genetically engineering cats could be a solution to eliminating cat allergies.
One-horned rhino population increases by 200 in four years
A census of the one-horned rhino population at Kaziranga National Park found that the vulnerable species is on the rise.
World’s largest bee, thought to be extinct, found in Indonesia
The giant bee was first discovered in 1859, but since has only officially sighted once. Now, researchers have found a specimen alive and well.
Squid skin inspires heat-regulating coffee cup
Inspired by squid skin, UC Irvine engineers have created a cheap, easy-to-recycle material that can be “tuned” to regulate heat.
3D-printed prosthetic helps big bird beat cancer
After removing part of a great hornbill bird’s casque, Florida veterinarians replaced it with a 3D-printed prosthetic.
This bird-like drone can perch on branches, catch objects
Inspired by birds' perching abilities, researchers developed a drone with a bird-like structure that can land on a wide array of objects.
Your pet dog could help people live longer, healthier lives
The Dog Aging Project is studying tens of thousands of dogs in the hope of helping pets and people live longer, healthier lives.
Internet-connected “smart” traps help cities combat rats
Internet-connected rat traps are bringing rodent control into the 21st century, helping cities leverage data in the battle against rats.
Californian wineries turn to owls as answer for growing pest problem
Rather than turning to rodenticides to deter pests, a new study is testing the effectiveness of owls to manage the problem.
Mammals dream about the world they are entering even before birth
A study finds that baby mammals dream about the world they are about to experience to prepare their senses.
Elephant tusk DNA is used to expose poaching networks
Researchers using cell phone records, shipment logs, and elephant DNA have solved poaching mysteries and identified trafficking networks across the continent.
Fossil of oldest octopus and vampire squid relative may reveal 10-armed past
A newly described fossil may be the oldest relative yet found of octopuses and vampire squids — although if it is a new species at all is disputed.
New children’s malaria treatment clears out infection in liver
Malaria can hide in the liver, causing relapse months or years later. Now, public health officials have a new treatment to prevent relapse for children under 16.
Digital sound archives can bring extinct birds (briefly) back to life
Sound recordings remind us that these beings are invaluable, and that humans have a duty to preserve them.
Pregnant dolphins identified by drones for the first time
Using drone photography, University of Aberdeen researchers have been able to identify pregnant dolphins for the first time.
New breed of pig will provide organs for human transplantation
German researchers are breeding a new type of pig that’s been genetically modified to have organs ideal for human transplantation.
Hibernating squirrels hint at secret to surviving space travel
Astronauts lose muscle mass in space. The secret to how ground squirrels keep mass in hibernation may help future space travelers keep their own.
“BioDome” triggers near-complete limb regeneration in frogs
A new limb regeneration treatment allowed adult African clawed frogs to regrow near-complete functional legs following amputation.