Field: Medicine
An international team sets out to cure genetic heart diseases with one shot
Researchers from the UK, US, and Singapore are beginning work on a genetic heart cure they hope to begin clinically testing within five years.
Researchers may have created a universal coronavirus vaccine
All currently licensed COVID-19 vaccines target the spike protein’s S1 region, which is prone to mutations. We need a universal vaccine.
Pfizer’s RSV vaccine is 86% effective at preventing severe illness
According to a huge phase 3 trial, Pfizer’s RSV vaccine is nearly 86% effective at preventing severe illness in older adults.
Scientists convert kidney to universal “O” blood type
Kidneys still need to be tissue matched, but by converting them to type O, more will be available for transplant.
New epilepsy treatment could stop seizures in their tracks
A new epilepsy treatment that's delivered as a nasal spray may be able to prevent seizures or even interrupt them.
A sepsis-catching AI has proven effective in hospitals
A new AI for spotting sepsis, which accounts for ⅓ of hospital deaths, was found to be effective in a large trial.
What smart toilet seats reveal about digital health’s evolution
Digital health is attracting record levels of investment in products such as smart toilet seats, which can help millions get access to care.
First personalized CRISPR therapy approved for trial
The FDA has approved a trial for the first personalized CRISPR therapy, which was developed to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Light pulses can stop dangerous food poisoning like Salmonella
A team at Penn State has developed a pulsed light technique capable of killing common food poisoning pathogens.
Synthetic cartilage is now stronger than the real stuff
Using a heating process, Duke researchers have created a synthetic cartilage hydrogel that can outperform the real thing.
New kind of schizophrenia drug aces human trial
KarXT, a new schizophrenia treatment that addresses a wider range of symptoms than existing meds, has aced a phase 3 trial.
Viruses may one day treat inflammatory bowel disease
Researchers have created a cocktail of viruses that may be able to treat inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s.
Nanoparticle sensor can distinguish between viral and bacterial pneumonia
MIT researchers have designed a sensor that can distinguish between viral and bacterial pneumonia infections.
Yale study finds low levels of a hormone may predict long COVID
Yale and Icahn School of Medicine researchers may have found biomarkers for identifying long COVID.
Only human Lyme vaccine in development enters phase 3 trial
Pfizer and French biotech Valneva have announced a phase 3 clinical trial testing the human Lyme vaccine.
Half of all vaccines are wasted. A gel could save them.
A new hydrogel that wraps around heat-sensitive molecules could help prevent vaccine waste by keeping them viable at higher temperatures.
What ever happened to the first cryogenically frozen humans?
For decades, people have arranged to freeze their bodies after death, dreaming of resurrection by advanced future medicine.
A new drug could repair stroke damage to memory and movement
A new drug can repair stroke damage in mice, improving memory and motor skills. If it works in humans, it could lead to a paradigm shift in stroke treatment.
Long COVID-19 and chronic conditions after viral infections may stem from an overactive immune response
Understanding the immunological mechanisms underlying long COVID-19 is the first step to addressing a quickly worsening public health problem.
Why don't surgeons train like fighter pilots? Now some do.
Using AI and analysis, Theator is helping surgeons improve how pilots and pro athletes do: by going to the tape.
The Biden administration is preparing for legal psychedelics within two years
The Biden administration’s Department of Health and Human Services has sent a memo supportive of psychedelic therapies. What does that mean for the field?
ADHD drugs might also treat Alzheimer’s disease
Scientists reviewed 40 years of clinical studies that assessed the effects of NA-targeting drugs, such as certain ADHD drugs, on Alzheimer’s.
A cheap nasal spray cuts COVID-19 risk by 62%
A low-cost nasal spray co-developed by Oxford researchers could be the next powerful weapon against COVID-19.
Your genes may impact psychedelic experiences
UNC researchers have found evidence that the genetic makeup of a crucial receptor may impact your psychedelic experience.
Harvard scientists closer to solving centuries-old heart mystery
Harvard researchers have used a new method to crack the heart’s weird spiral muscle.
MIT engineers 3D-print rubbery brain implants that don’t “stab” the brain
How do you engineer an implant that doesn't harm an organ as soft as tofu? MIT engineers 3D-printed new soft brain implants.
How child mortality fell from 40% to 3.7% in 200 years
The collapse in child mortality rates is a testament to the tremendous benefits of scientific, technological, and economic progress.
Large study of 20,000 cats and dogs could help pets live longer
Mars Petcare has announced the opening of a massive biobank to study aging and pet diseases.
Potential cause of unexplained epilepsy cases uncovered
University of Arizona researchers have uncovered a protein that might be behind some epilepsy cases with currently unknown causes.
The first FDA-approved clinical trial of psilocin has begun
“This has never been done before,” says Filament’s CEO.
Nasal COVID-19 vaccines prepare for infection right where it starts – in your nose and throat
Intranasal vaccines are best suited to protect against pathogens that enter through the nose, like the flu or the coronavirus.
After death, you’re aware that you’ve died, say scientists
How can we know that we're dead after we die? Some evidence attributes a certain neurological phenomenon to a near death experience.
An old HIV drug may treat Down syndrome
A common HIV drug could potentially be a Down syndrome treatment, improving cognition in mouse models of the condition.
Nanoparticles may automatically clean your teeth one day
Shapeshifting nanoparticles may one day lead to automated oral care.
FDA may soon allow pig organ transplant trials
With pig transplantation looking increasingly viable, the FDA may soon allow clinical trials of the technique to begin.
Psychedelic research returns to Veterans Affairs
After decades, the Department of Veterans Affairs is once again investigating psychedelic therapies.
Universal flu vaccine enters phase 1 trials
NIAID researchers have begun a phase 1 trial of a new universal vaccine candidate that was promising in animal challenge studies.
A new delivery method for drugs that can’t withstand stomach acid
In order for a drug to get to the small intestine, it must first get past the highly acidic environment of the stomach.
Two FDA-approved drugs may improve Alzheimer’s symptoms
A retrospective study found that Alzheimer’s symptoms improved in patients who took two FDA-approved drugs that treat psychiatric disorders.
UK tries cancer meds by drone
The UK’s National Health Service (NHS) is using drone deliveries to make it easier for cancer patients to obtain chemotherapy.
He lost his baby daughter. Then he turned his grief into a tool for NICU parents.
After losing his daughter, a father found a way to help other NICU parents.
A dog cancer vaccine may save them and, one day, us
Dutch researchers have created a dog vaccine which may pave the way for similar human therapies.
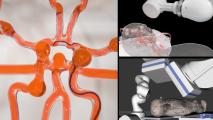
Magnetic robot can save lives after a brain hemorrhage
Researchers have developed a microbot-containing, magnetically controlled catheter for removing blood from brain hemorrhages.
CRISPR cure for sickle cell nearly 100% effective after three years
A CRISPR therapy for sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia looks close to 100% effective three years after infusion.
This molecule may be the “secret sauce” of exercise — but it won’t work as a pill
Administering Lac-Phe to obese mice significantly lowered their appetite, reduced body fat, and improved glucose tolerance.
CRISPR could create a one-shot treatment for HIV
Researchers have used gene editing to engineer HIV-fighting immune cells inside the bodies of mice.
Engineers develop nanoparticles that cross the blood-brain barrier
Tested using a new brain tissue model, the particles may be able to deliver chemotherapy drugs to cancer patients.
CRISPR can create a “captain’s log” for bacteria traveling through the microbiome
A team at ETH Zurich has modified E. coli to work like biological recorders of the processes of the gut.
Apple Watch now approved to track Parkinson’s symptoms
Apple Watch motion data will now be incorporated into Rune Labs’ StrivePD app, which tracks Parkinson’s symptoms.
Moms’ “super-antibodies” point the way to new antibody medicines
Pregnancy bestows on babies enhanced antibodies that can protect against a broader range of disease. Now, we know how.
A vaccine against mosquito saliva may be the key to stopping their diseases
University of Leeds researchers have identified a compound in mosquito saliva as a potential target to protect against multiple viruses.
A smart bomber for bacteria could help save antibiotics
Brown University researchers have developed a “smart” drug delivery system that only releases its payload when bacteria are present.
Handheld antibody tester could reveal if you’re immune to COVID
Hong Kong researchers have developed a handheld COVID antibody testing device more capable than current home tests.
Tiny nanoscale drills can bore holes right through bacteria
Rice University researchers have developed tiny, bacteria-boring drills in an effort to stop superbugs.
The key to fighting fungal infections may have been inside us all along
MIT researchers have discovered that complex molecules in mucus can keep fungal infections in check.
“Stealth bomb” for cancer unlocks powerful immune attack
A "masked" cancer drug stealthily trains immune system to kill tumors while sparing healthy tissues, reducing treatment side effects.
Gene therapy fixes rare heart disorder with clever workaround
Cleveland Clinic researchers have developed a gene therapy that cured arrhythmias in mice.
Stimulating deep sleep may improve brain health, memory, and mood
Researchers are trying to harness deep sleep to bolster the glymphatic system, which helps flush brain tissue.
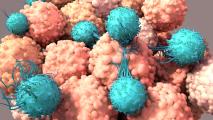
Small trial of cancer immunotherapy sends every patient into remission
Every participant in a small trial testing a rectal cancer immunotherapy has had their disease go into complete remission.
Three more nations eliminate sleeping sickness as a public health threat
Sleeping sickness is a horrifying disease mainly impacting the rural poor. But three more African nations have succeeded in curtailing its threat.
Nuclear isomers were discovered 100 years ago
Protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can be arranged in different configurations, creating nuclear isomers.
Why at-home STI tests may (finally) be about to take off
Inspired by the home testing of the pandemic and rising STI cases, some experts think that more accessible testing may be an important public health tool.
This already-approved drug could help repair the brain after stroke
Ohio State researchers have found that an already approved anticonvulsant drug helps increase stroke recovery in mice.
New surgery implants living, 3D-printed body parts
A 3D-printed outer ear made from the patient’s own cells has been implanted.
Genetic mutations can be benign or cancerous – here’s a new way to identify them
Identifying the difference between normal genetic variation and disease-causing mutations is vital for determining a person's treatment.
HIV drug could improve memory
The common HIV drug maraviroc improved memory linking in aging mice and might be able to help people experiencing memory loss, too.
The source of a strange anti-cancer compound is found in Florida
Researchers have discovered that common soft corals are the source of a sought-after anti-cancer compound.
New tech could help prevent 2/3 of hospital-acquired infections
A new treatment could prevent hospital-acquired infections by making it hard for biofilms to form on implanted medical devices.
What is monkeypox, and how we may fight it
As monkeypox cases crop up around the world, vaccines designed for the far deadlier smallpox may play a key role in stopping it.
Ultrathin fuel cell uses the body’s own sugar to generate electricity
Batteries have a limit to how small they can be made, and they need to be charged. What if you could power your own medical device?
New drug combo is “a paradigm shift” in preventing asthma attacks
The combination of a rescue medication and a corticosteroid, taken as needed, reduced both short and long-term risk of asthma attacks.
Nanoparticles are the future of medicine
The success of some drugs that use nanoparticles, such as the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, has prompted excitement among researchers.
Nanobots are real, and they can battle bacteria
Researchers have developed antibiotic nanobots that can traverse a wound on their own.
Will new vaccines be better at fighting coronavirus variants?
New virus-based vaccines could play an important role in generating a long-lasting, broad immunity against a rapidly mutating virus.
How we treat inflammation may be causing chronic pain
Reversing common belief, researchers at McGill say treating inflammation may be causing chronic pain, not preventing it.
Silkworms could one day repair human tendons stronger than before
Mixing silk protein with a gel matrix allowed for better cell growth and healing in rat models.
Nonprofit drugmaker Civica Rx is taking aim at the high insulin price
People living with insulin-dependent diabetes have been waiting a long time for it to be more affordable. Could things change?
Brain infusions from younger mice revive memory in older ones
Stanford researchers have found that an infusion of cerebrospinal fluid from young mice improves the memory of old ones.
New vaccine for Epstein-Barr virus enters human trials
A Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) vaccine entering human trials could potentially protect against everything from mono to multiple sclerosis.
How herpes wakes up
Researchers believe they have identified how herpes hiding in your cells wakes back up to cause symptoms.
Genes from over 5,000 stroke patients hint at surprising treatment
A study of nearly 6,000 stroke patient genomes suggests a treatment idea abandoned for decades should get a second look.
Moderna expects to have Omicron booster ready by Fall 2022
Moderna expects to have an Omicron booster that combines its original COVID-19 vaccine with one targeting the variant ready by Fall 2022.
5G millimeter wave tech may prevent unnecessary skin biopsies
Stevens Tech researchers have developed a device which uses the same tech as the TSA does to find skin cancer tissue without a biopsy.
A Spanish teen’s genome may hold the secret to lupus
Researchers believe they have found a single point mutation in an infection-sensing gene that causes the autoimmune disorder.
Surprise in death data: Malaria has a U-shaped death curve
Better death records can reveal surprises about common killers like malaria — and help save lives.
Rebreather dives are wildly risky. But this might save lives.
Duke researchers have developed an early warning system for rebreather divers at risk of hypoxia.
Joystick-operated robot could help surgeons treat stroke remotely
With a modified joystick, surgeons in one hospital may control a robotic arm at another location to safely operate on a patient.
How Robert Langer, a pioneer in delivering mRNA into the body, failed repeatedly but kept going
Langer published the first paper to show that it was possible to deliver nucleic acids like RNA and DNA to the body via tiny particles.
RNA breakthrough offers a potential heart attack cure
King’s College London researchers have used RNA to regenerate cardiac tissue in pig hearts, what they hope is the first step towards a heart attack cure.
Researchers want to fight cancer — by mutating it even more
Sloan Kettering researchers have proposed a controversial way to improve immunotherapy: making cancer cells mutate on purpose.
Moderna applies for approval of COVID-19 vaccine for children
Moderna has asked the FDA to authorize its COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 6 months through 5 years.
America’s “Test to Treat” has failed. Here’s how to fix it.
So far, Test to Treat has largely failed to get antivirals for COVID-19 to patients that need them — but the initiative can still be fixed.
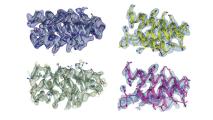
Computer-designed miniproteins unleash a whole new kind of drugs
Using a computer program, researchers have created miniproteins that they hope can lead to new drugs.
T cells and viruses, an unlikely duo, team up to kill tumors
A new Mayo Clinic-developed immunotherapy combining CAR-T cells and cancer-killing viruses looks promising in mouse models.
Drug to treat alcoholism could also safely reduce anxiety
The alcoholism treatment disulfiram may be able to serve double-duty as an anti-anxiety medication, according to mouse studies.
Bacteria living inside tumors help cancer spread through the blood
Intracellular bacteria promote cancer metastasis by enhancing the tumor cells' resistance to mechanical stress in the bloodstream.
New $5-device allows healthy sperm cells to isolate themselves
About 10% of men are infertile, and often their sperm is to blame. This device could help separate the healthy cells from the others.
Meningitis vaccine appears to protect against gonorrhea, too
Young people who received a meningitis vaccine appeared to be protected against the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea, too.
A “magnetic tentacle robot” could hunt down cancer deep in your lungs
UK researchers have developed a small, flexible, snake-like "magnetic tentacle robot" to navigate deep into the lungs.